The horse and its rider slowly trot down the town’s main street, stopping at the saloon, the kind of bar particularly to the old west. The man tips his cowboy hat, dismounts and kicks open the swinging wooden doors. Inside everyone falls silent at the site of the cigar chomping, trigger happy cowboy. A familiar scene from most Clint Eastwood movies of the 80’s, the saloons usually have a loud, boisterous atmosphere in fictional depiction.
In truth, saloons, taverns and inns have long been integral to human socialization, serving as more than just places to enjoy a drink. Throughout history, these establishments have played diverse roles in shaping cultures, fostering community, and even influencing political landscapes.
A Tale as Old as Time
Tracing back to ancient civilizations, taverns emerged as communal hubs where individuals gathered to share stories, discuss matters of importance, and partake in libations. In places like ancient Greece and Rome, taverns served as meeting points for philosophical debates and political discussions, fostering a sense of camaraderie among citizens.
If you are a fan of Game of Thrones or fiction set in medieval times, you can’t help but note the important roles that taverns, innkeepers or a golden hearted buxom wench of ill-repute play in keeping the narrative interesting!
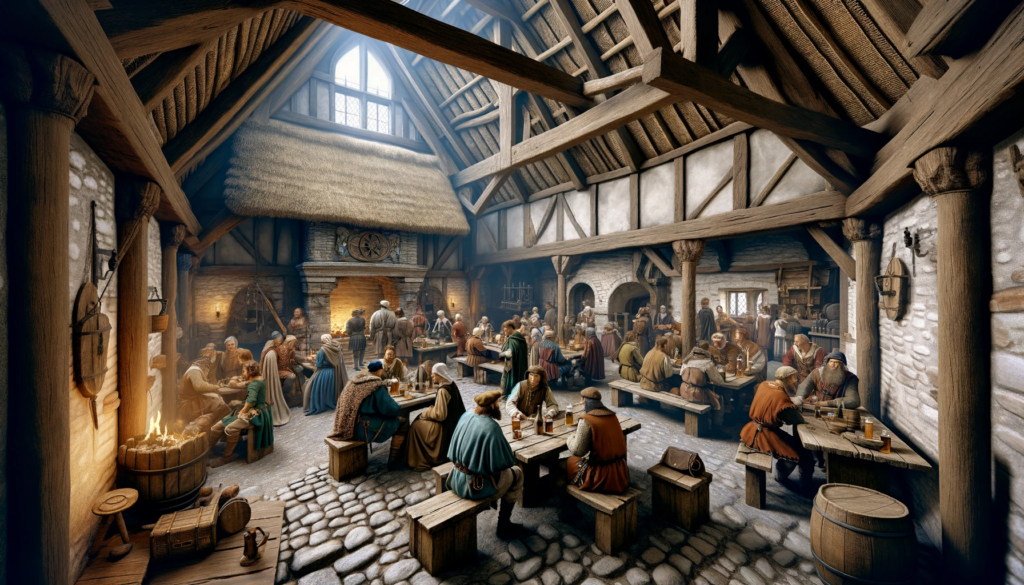
During the Middle Ages, taverns evolved into vital centers for both socializing and trade. Located along major trade routes, these establishments became essential stops for weary travelers, offering not only refreshment but also a place to exchange news and goods. In Europe, taverns often played a crucial role in the development of local economies.

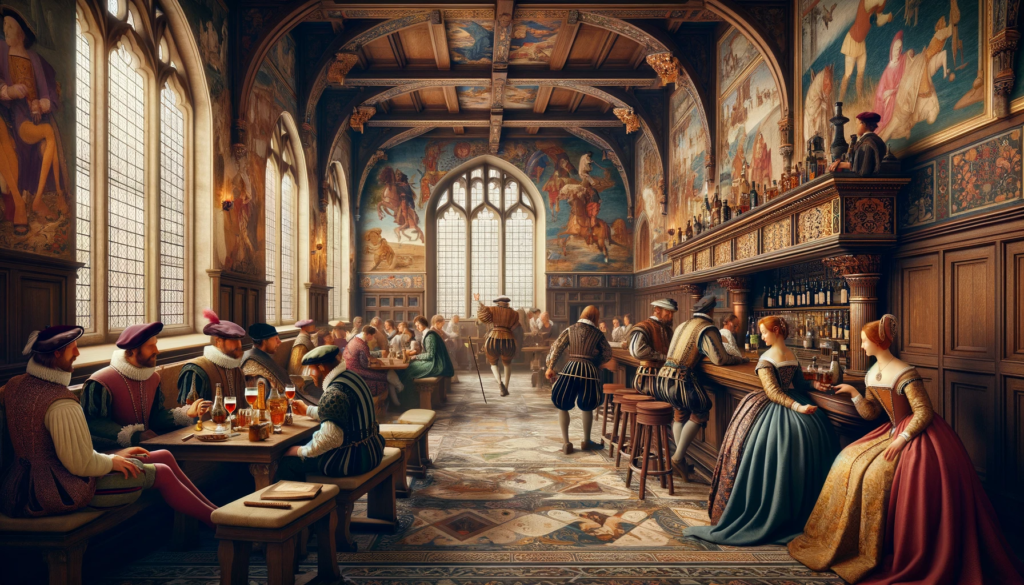
As the world entered the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, taverns continued to thrive as intellectual hubs. Thinkers and artists frequented these establishments, engaging in spirited discussions that contributed to the exchange of ideas.
In Colonial America, taverns played a pivotal role in shaping the social fabric of burgeoning communities. These establishments provided not only a space for socializing but also served as meeting places for early American revolutionaries to plan and strategize. Taverns became hotbeds for political discourse, helping to fuel the revolutionary spirit that led to the birth of a nation.

The Working Class Escapism
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes to the landscape of taverns. With the rise of urbanization and the growth of industrial cities, taverns transformed into spaces where workers sought solace and camaraderie after long, grueling days in factories. The pub culture of England and the tavern tradition in the United States continued to evolve, adapting to the changing needs of society.
In the 20th century, taverns took on various forms, from the speakeasies of the Prohibition era to the vibrant pub culture in many countries. Despite societal shifts, taverns retained their role as gathering places, adapting to modern trends while preserving their historical significance.
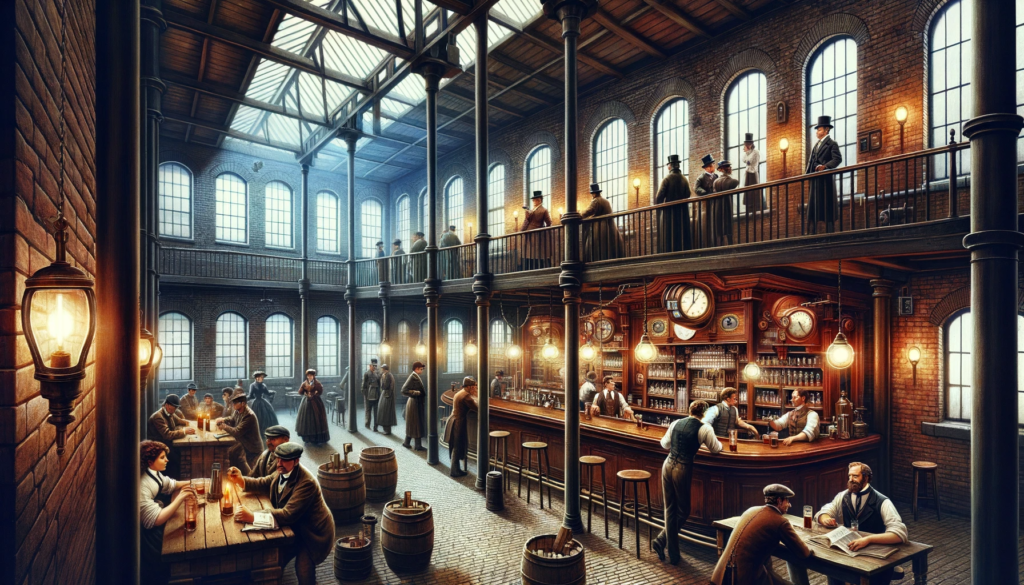

From Saraais to the Pubs
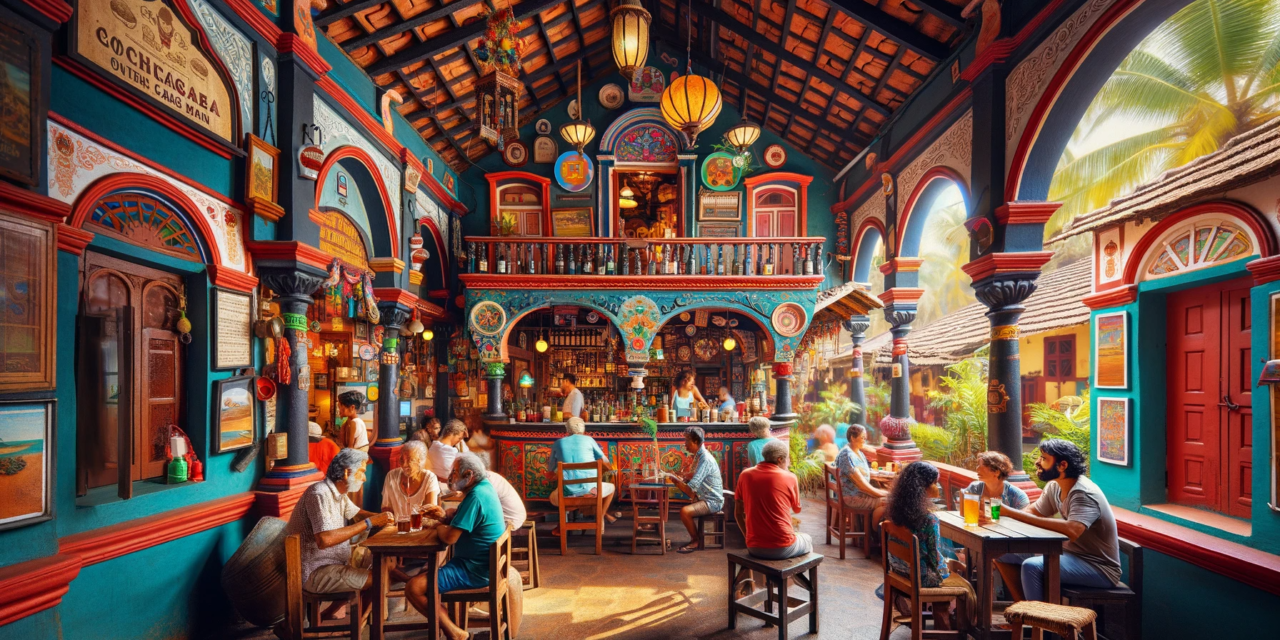
The history of taverns in India is a fascinating journey, reflecting the diverse cultural, social, and historical tapestry of the subcontinent. From ancient times to the present day, these drinking establishments have played unique roles, mirroring the evolution of society, trade, and cultural exchange.
In ancient India, the concept of communal gathering spaces for drinks dates back to Vedic times. Soma, an ancient intoxicating beverage, was consumed during religious rituals and social celebrations. As trade routes expanded, so did the exchange of alcoholic beverages, laying the foundation for early tavern-like establishments.
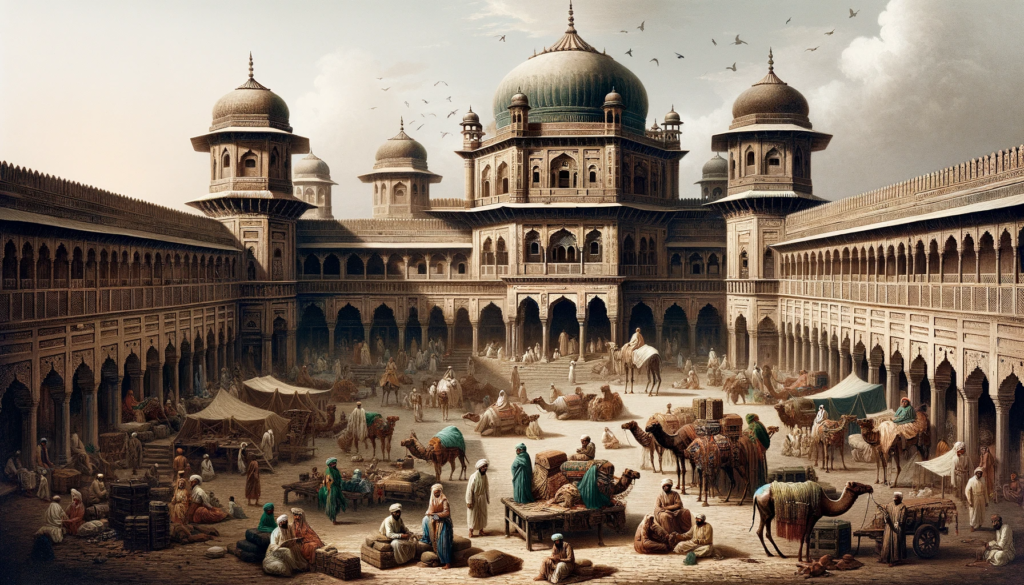
The Mughal era brought a distinct flavor to the tavern culture in India. The opulent courts of Mughal emperors often hosted grand feasts with an array of exotic drinks. Taverns, known as “saraais,” were established along trade routes to cater to travelers and traders. These spaces served as meeting points for cultural exchange and the sharing of stories.

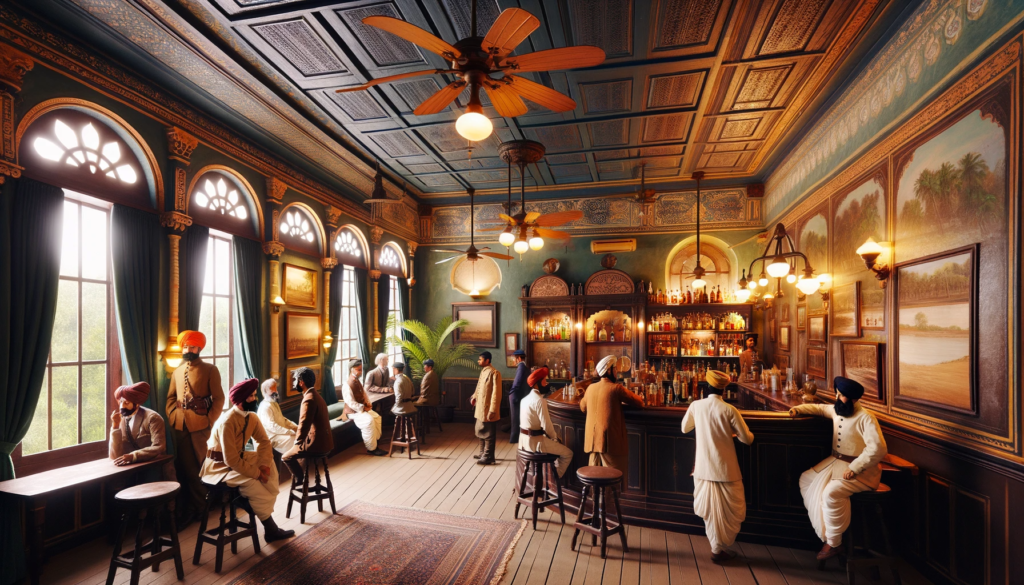
With the arrival of European colonizers, tavern culture underwent transformations. The British, in particular, introduced pubs and taverns to cater to the growing expatriate and military communities. The local populace also embraced these establishments, leading to the fusion of British pub traditions with indigenous drinking customs.
After India gained independence, taverns continued to evolve. The concept of the “local bar” became widespread, offering a casual setting for socializing. The diversity of India’s regions is reflected in the wide array of local beverages served, showcasing regional specialties.

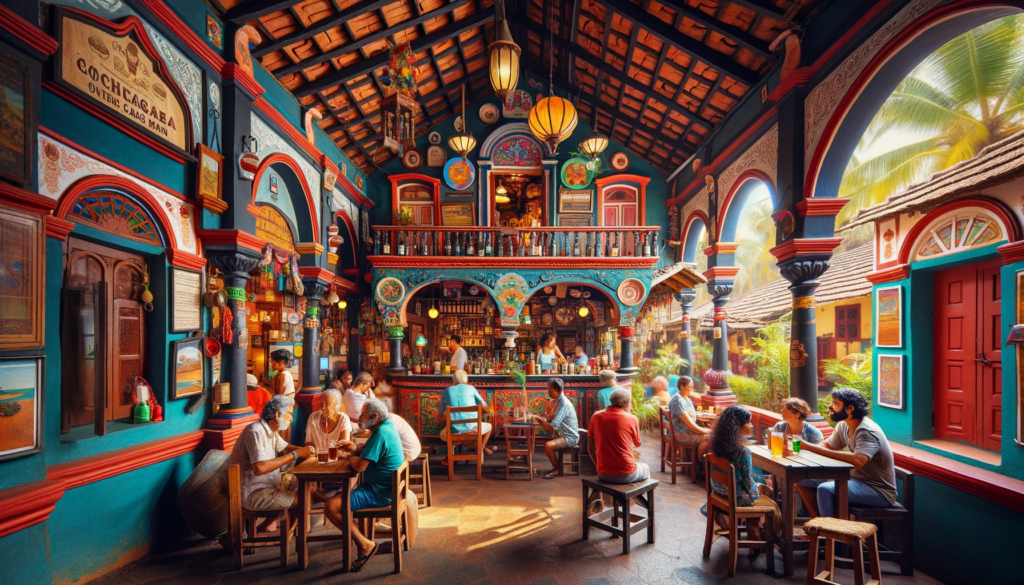
Over the years, India has witnessed changes in alcohol regulations, impacting the tavern landscape. The prohibition era in certain states, coupled with varying state-level regulations, has influenced the nature of drinking establishments. Despite these challenges, taverns persist as integral components of urban and rural social life.
In contemporary India, the tavern scene is vibrant and varied. From the traditional “tharra shops” in rural areas to the chic bars in metropolitan cities, drinking establishments cater to a diverse clientele. The emergence of craft breweries and the revival of traditional brewing methods further contribute to the richness of India’s tavern culture.

The history of taverns is a rich tapestry woven into the fabric of human civilization. Today, taverns continue to stand as testaments to the enduring human need for communal spaces that foster connection, conversation, and shared experiences.